

#FIXED ASSET TURNOVER INTERPRETATION CODE#
Their database is sorted by the North American Industrial Classification System (NAICS) code and contains both national and regional data. Their database is 700+ industries strong and compiles data from documents such as balance sheets, income statement line items, and close to 19 different ratios. It is the only source of financial ratio benchmarks directly derived from over 250,000 financial statements of contributing member clients. They are best known for publishing meticulously curated comparative industry benchmark data reports, which is popularly known as the Annual Statement Studies®.
The Risk Management Association (RMA) is a member-driven non-profit that focuses on compiling financial data. Common Industry Benchmark databases for Financial Ratios It is up to a financial analyst to use trend analysis, common size analysis, and ratio analysis to compare the subject company and the selected benchmarks in order to create a reliable multiple. Industry benchmarks are either derived from these company-driven multiples or from credible industry benchmark databases. Using Financial Ratios in benchmarking business valuationsĬompanies generally use certain guidelines to derive multiples. The various types of debt ratios help determine factors such as the amount of company assets provided through debt, weight of the total debt and financial liabilities against shareholder’s equity, the company’s ease in paying interest expenses, and the ease with which a company will pay its debt obligations. Leverage financial ratios – These financial ratios indicate the company’s debt levels. Different types of market value ratios help determine trends such as the per-share value based on available equity, the dividends shareholders will receive compared to the market value per-share, the net income earned for each outstanding shares, and the share price of the company as compared to its earning per-share. Market value ratios – These financial ratios help analyze the share price of a company. Average collection period= 365 days / Accounts Receivable turnover. Accounts receivable turnover ratio= Net sales / Average Accounts Receivables. Total Asset Turnover ratio= Net sales/ total assets. Annual inventory turnover ratio= Cost of good sold/average inventory. Outside the company: Financial analysts, security analysts, competitors, investors, creditors, tax and regulatory authorities. Within the company: Founders, management team, and employees. A competent financial analyst will refer to a good mix of ratios before arriving at any conclusion.įinancial ratios are primarily used by two categories of people: However, considering a stand-alone ratio can be misleading. This helps management spot problematic areas in the very early stages. 
These ratios are derived by dividing one financial measurement by the other.įinancial ratios serve as an important tracking tool for identifying trends and discrepancies in the company’s finances. In simple terms, financial ratios are the relationship established between various statistical data provided in the company’s financial documents such as the balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statements, etc. As important as they are as a document, the numbers in these statements alone are not capable of indicating any underlying issues, risk trends, or a probable future performance, unless they are analyzed properly. The performance of a business is ultimately reflected in their periodic financial statements.
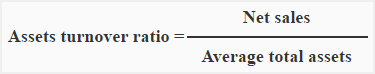
We have also compiled a comprehensive database of the IRS financial ratios by industry which will act as quick reference for your respective businesses. In this article, we will explore the idea of financial ratios with a deeper insight into some of the basic types of ratios. Analysts, investors, creditors, and all other lending institutions rely on these ratios to gauge a company’s footing in the business. Financial ratios are the cornerstone of any company valuation.




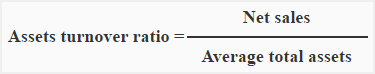


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
